The Evolution of Television: From Black-and-White to the Digital Age
Television is one of the most influential inventions in modern human history. It has shaped how people receive information, experience entertainment, understand global events, and connect with culture. From its early experimental days in the late 19th century to today’s ultra-high-definition smart televisions, TV technology has continuously evolved alongside scientific innovation and societal change.
The evolution of television is not a single moment of invention but a long journey involving many scientists, engineers, and creative thinkers. Each era of television reflects the technological capabilities, cultural priorities, and communication needs of its time.
Early Concepts and Theoretical Foundations (Late 1800s)
Paul Nipkow and the Mechanical Scanning Idea
In 1884, German engineer Paul Gottlieb Nipkow patented the Nipkow Disk, a mechanical scanning device that could transmit images by breaking them into lines. Although primitive, this invention laid the theoretical foundation for television.

At this stage:
- Images were low-resolution
- Transmission was mechanical, not electronic
- No practical broadcast system existed
Still, Nipkow’s idea introduced the essential principle of image scanning, which remains fundamental even in modern digital TVs.
Mechanical Television Era (1900–1930)
Early Experiments
Between 1900 and 1930, several inventors attempted to turn theory into reality using mechanical systems.
Notable contributors:
- John Logie Baird (Scotland)
- Charles Francis Jenkins (USA)
In 1925, Baird successfully demonstrated the first moving television images. By 1926, he showcased the world’s first public television demonstration.
Limitations of Mechanical Television
- Very low image quality
- Flickering visuals
- Poor synchronization
- Large, noisy mechanical components
Despite its flaws, mechanical television proved that visual broadcasting was possible.
The Birth of Electronic Television (1930s)
Key Inventors
The real breakthrough came with electronic television, replacing mechanical parts with electronic circuits.

Important figures:
- Philo Farnsworth – Developed the first fully electronic TV system
- Vladimir Zworykin – Invented the Iconoscope camera tube
Electronic television allowed:
- Higher resolution
- Stable images
- Faster transmission
- Scalability for mass broadcasting
First Regular Broadcasts
By the late 1930s:
- BBC began regular television broadcasts (1936)
- RCA promoted TV technology in the United States
Television was now becoming a commercial reality.
Television Interrupted: World War II (1939–1945)
World War II halted television development in many countries. Factories shifted to military production, and broadcasting resources were redirected toward war communication.
However, wartime research indirectly advanced:
- Electronics
- Radar technology
- Signal transmission
These advancements later benefited television technology.
The Golden Age of Black-and-White Television (1945–1950s)
Post-War Expansion
After World War II, television ownership grew rapidly, especially in the United States and Europe.
Key features:
- Black-and-white screens
- Vacuum tube technology
- Antennas for signal reception
Television became:
- A family activity
- A major news source
- A powerful cultural influence
Popular content included:
- Live news broadcasts
- Sitcoms
- Variety shows
- Sports events
The Introduction of Color Television (1950s–1960s)
Development of Color Broadcasting
Color television transformed the viewing experience.

Milestones:
- 1953: NTSC color standard approved in the USA
- 1960s: Color TV becomes commercially viable
Initially:
- Color TVs were expensive
- Broadcasts were limited
By the late 1960s:
- Color became the standard
- Black-and-white TVs began disappearing
Color television enhanced realism and emotional engagement, changing entertainment forever.
The Rise of Cable and Satellite Television (1970s–1980s)
Cable Television (CATV)
Cable TV was introduced to improve reception in remote areas, but it soon expanded content variety.
Benefits:
- More channels
- Better signal quality
- Specialized programming
Satellite Television
Satellite technology allowed:
- Global broadcasting
- Live international events
- 24-hour news coverage
This era saw the birth of:
- CNN (24-hour news)
- MTV (music television)
- ESPN (sports broadcasting)
Television became more diverse and global.
Remote Control, VCRs, and Home Entertainment (1980s)
Technological advancements changed viewer behavior.

Key Innovations
- Remote controls
- Video Cassette Recorders (VCRs)
- Home video rentals
Viewers could now:
- Change channels instantly
- Record programs
- Watch content on demand (early form)
Television shifted from passive viewing to user-controlled entertainment.
Digital Television Revolution (1990s)
Analog to Digital Transition
Digital television replaced analog signals, offering:
- Clearer images
- Better sound
- Efficient bandwidth use
Major developments:
- High-Definition Television (HDTV)
- Flat-panel displays (LCD, Plasma)
Governments worldwide gradually phased out analog broadcasting.
Digital TV laid the groundwork for future smart technologies.
Flat-Screen and High-Definition Era (2000s)
Technological Advances
- LCD and Plasma TVs
- Later, LED displays
- Slim and lightweight designs
Screen quality improved dramatically:
- HD (720p, 1080p)
- Widescreen formats
Televisions became:
- Wall-mounted
- Stylish home décor elements
- Energy-efficient
Smart Television and Internet Integration (2010s)
The Smart TV Revolution
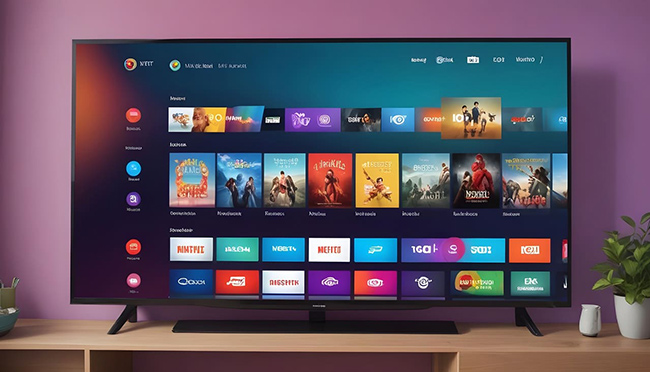
Smart TVs integrated:
- Internet connectivity
- Apps and streaming platforms
- Voice control and AI features
Popular platforms:
- Netflix
- YouTube
- Amazon Prime Video
Viewers shifted from scheduled programming to on-demand streaming.
Television became a multimedia hub, not just a broadcast device.
Ultra-High Definition and Display Innovations (2020s)
Modern TV Technologies
- 4K and 8K resolution
- OLED and QLED displays
- HDR (High Dynamic Range)
Advantages:
- Incredible color accuracy
- Deep blacks
- Cinematic viewing experience
AI and Personalization
Modern TVs use AI to:
- Upscale content
- Recommend shows
- Optimize sound and picture
The Cultural and Social Impact of Television
Television has:
- Shaped public opinion
- Influenced fashion and language
- Connected global audiences
- Played a role in education and awareness
From moon landings to global pandemics, TV has documented history in real time.
The Future of Television
Emerging trends include:
- Virtual Reality (VR)
- Augmented Reality (AR)
- Holographic displays
- Fully personalized content
Television is evolving into an immersive, interactive experience beyond traditional screens.
The evolution of television reflects humanity’s constant desire to communicate, entertain, and understand the world visually. From mechanical disks to AI-powered smart screens, television has undergone remarkable transformation.
Despite competition from mobile devices and social media, television continues to adapt and remain relevant. As technology advances, television will not disappear—it will evolve, just as it always has.
Television is no longer just a device, it is a living medium that grows with human imagination.
Sources
BBC History. The History of Television.
Smithsonian Institution. Television and the Digital Era.
U.S. National Archives. Television History and Technology.
Encyclopaedia Britannica. Television: History and Development.
Burns, R. W. Television: An International History of the Formative Years. IET, 1998.

